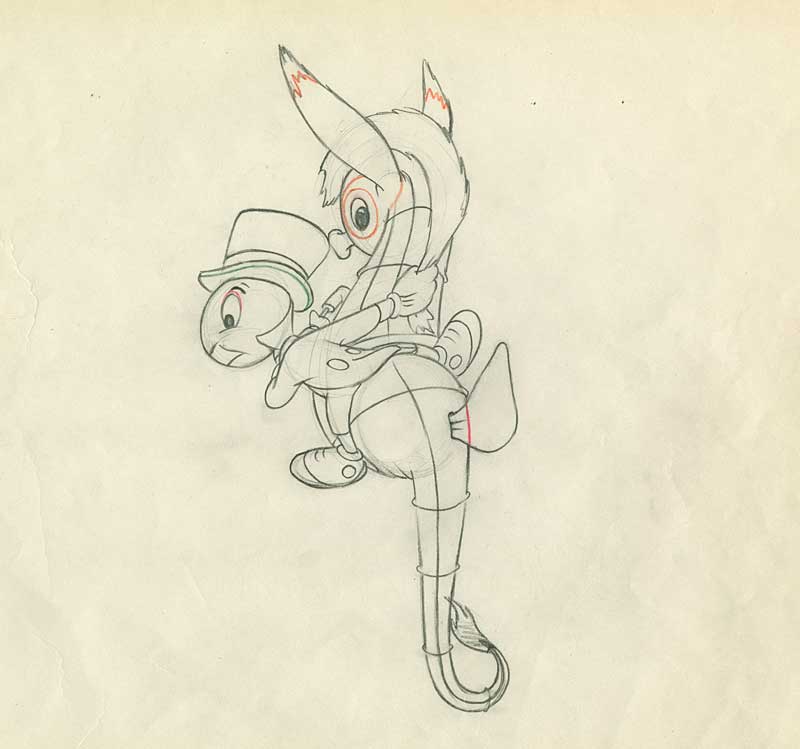
As a special thank you to our annual General and Student members, we have created a special page where we will archive past Reference Packs. There will be at least four reruns of complete RefPacks per year.
If you are currently on a quarterly membership plan, consider upgrading to an annual membership to get access to our bonus page with even more downloads. If you still have time on you quarterly membership when you upgrade to an annual membership, email us at…
membership@animationresources.org
…and we will credit your membership with the additional time.
Available to Student and General Members
PDF E-BOOK:
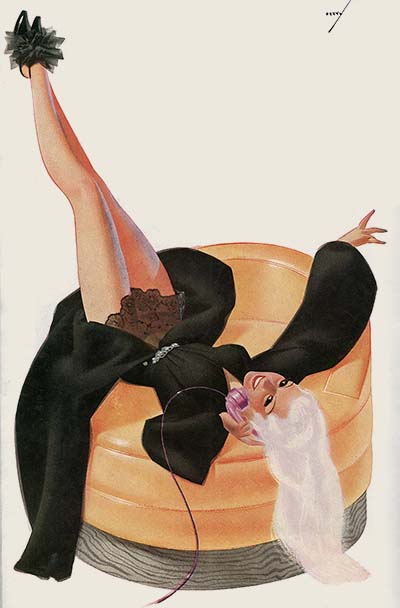

Esquire Magazine![]()
Cartoon Annual Volume 1 (1937)
Esquire was the leading "gentleman’s magazine" of its day. Great writers like F. Scott Fitzgerald and Ernest Hemmingway wrote for the magazine, and the Esquire staff included a stable of illustrators and cartoonists that represented the best in the field. Even though it was founded in the height of the depression, the publishers spared no expense to produce a first class product. The cover price was fifty cents, many times the price of any other magazine on newsstands at the time. Hugh Hefner began his career as a copy editor at Esquire in the late forties, and it’s clear that his vision of what Playboy would become was greatly influenced by Esquire.
In 1937, the staff of Esquire prepared a prototype copy of a proposed cartoon annual containing the best cartoons from the first few years of the magazine’s publication. However before the book could be printed, the project was cancelled and the prototype was put on the shelf. Twenty years later, they finally did publish a book honoring the great work of the Esquire art staff, but it was a much different selection of cartoons. Animation Resources was given access to the one-of-a-kind prototype of the 1937 book, and we will be sharing it with our members in this, the first of two e-books. We hope you find it to be useful.
Click to access the…
Downloads expire after September 2022
DVD QUALITY VIDEO:![]()

The Mascot![]()
(Ladislas Starevich/1933)
Ladislas Starevich created the first puppet animation film in 1912 and continued to work in the medium for half a century. He was born in Russia to Polish parents in 1882 and emigrated to France soon after World War I. Assisted by his wife, who made the costumes for the puppets, as well as his daughter and son, Starevich produced a large and varied filmography. We are presenting the most famous of his films, "The Mascot", which Terry Gilliam has cited as one of the ten greatest animated films of all time.
"The Mascot" (1933) is a technical marvel, with sophisticated puppet armatures, a wide variety of techniques, and fantastic subject matter. Starevich simulated motion blur in this film by smearing vaseline on a glass plate between the camera and the puppet. He also broke new ground by rigging the puppets so they could move slightly while the shot was being exposed. This technique predated Jim Danforth’s "Go Motion" in the Star Wars films by almost 50 years! We have deinterlaced this film and encoded it at an increased bitrate so you can step frame through the animation and study the animation. Starewich often created a seamless blend of several different techniques in a single shot. It’s fascinating to look at the work frame by frame to discover the secrets behind the cinematic magic.
"The Mascot" was edited and reformatted several times over the years. It is rarely seen with the original soundtrack and running time, but Animation Resources obtained a copy of the film as it was first released and we are proud to be able to share that with you. If you would like to see more films by Starevich, let us know on the Animation Resources Facebook page.
Click to access the…
Downloads expire after September 2022
DVD QUALITY VIDEO:![]()

Two Fleischer Screen Songs![]()
“Tune Up And Sing” (1934) “Let’s All Sing Like The Birdies Sing” (1934)
When the Hayes Office took aim at risqué humor in the movies, Fleischer’s Betty Boop cartoons were square in its crosshairs. The difference between the 1933 Betty Boop cartoons and the ones from 1934 is stark, and the series never really recovered from the blow. The Screen Songs weren’t hit nearly as hard, but you can still see that when it comes to gags, punches are being pulled. To add insult to injury, when these cartoons were syndicated to television in the late 1950s, the live action celebrity cameos and singalong sequences were usually cut out, and that is the case with the two examples we are sharing in this Reference Pack. But because of the way the cartoons were constructed, the edit isn’t too noticeable and they play well as short cartoons.
In the home video era, the Fleischer Screen Songs cartoons are missing in action. Only a tiny handful have been released. Animation Resources would like to thank our Advisory Board Member, Steve Stanchfield for sharing these rare films with us.
Click to access the…
Downloads expire after September 2022
More members mean we can bring you more special downloads.

Animation Resources is asking our membership to consider donating to help us establish a video podcasting studio to be able to present seminars, interviews and informal updates live streamed on YouTube and Facebook. Our goal is for 25 of our members and supporters to donate $100. If you donate $100, we will provide you with a coupon code for a free membership to give as a gift to a friend or peer, or we can credit your donation to sponsor two students for a one year student membership.
By helping others, you help yourself.

Please consider donating using the PayPal Donate Button below. For more information on our Video Podcasting Fundraiser, see the article Animation Resources Needs Your Help.
![]()
![]() Animation Resources depends on your contributions to support its projects. Even if you can’t afford to donate $100 or join our group right now, please click the button below to donate whatever you can afford using PayPal. Every little bit helps.
Animation Resources depends on your contributions to support its projects. Even if you can’t afford to donate $100 or join our group right now, please click the button below to donate whatever you can afford using PayPal. Every little bit helps.

Or you can donate on Facebook, here…
FACEBOOK LIVESTREAM FUNDRAISER
After you have donated, drop us an email at sworth@animationresources.org and let us know if you would like a discount code for a free membership, or if you would like us to sponsor students with your donation.
Raising the bar with our live streaming initiative will make things better for the whole art form. Don’t stay on the sidelines. Be a part of Animation Resources and join our team to build the foundation for the future of animation.