Assistant Archivist, JoJo Baptista brought in some magazines for the archive donated by his teacher, and long-time archive supporter, Dave Brain. Among them was an AFI publication with this great article by Chuck Jones…
ANIMATION IS A GIFT WORD
By Chuck Jones
A young man was once sent fresh from Columbia University with a mutual friend’s introduction to Robert Frost. Frost scanned the young man’s writings, then looking quizzically up through his craggy white brows he asked, “What do you do, son?” The young man drew himself up proudly; he was, after all, one with the great Frost. “I am a poet,” he said. Frost gently answered, “The term ‘poet’ is a gift word, son; you cannot give it to yourself.”
The term “artist” or “animator” are gift words too, and yet they are employed as self-description by an astonishing number of our colleagues.

The Marx Brothers, Laurel & Hardy, Harold Lloyd, W.C. Fields, as well as Chaplin, are now considered to be artists, but I grew up in Hollywood when they were in the height of their power and I know that the term would have staggered and surprised them. They were honestly and simply trying to make funny pictures and were about as aware of dramatic and comedic theory as a bunch of otters. They were a joyous, funny, often drunken, usually wild and impetuous group and all I wanted in the whole world when I grew up was to be one of them. This horrified my mother, who felt that the mayhem and violence of the Keystone Cops, Larry Semon and even Chaplin when, for instance, he gassed or blew people up, was hideous fare for my budding libido.

She was right. When I did kind of grow up my hideously budded libido found that the one-reel comedy was no longer around, but I managed to stumble into another company of comedians who would have been just as unaware as their great live-action predecessors to find themselves characterized as “artists”: the animators. Tex Avery, Friz Freleng, Ham Hamilton, Hugh Harman and Rudy Ising, Hanna and Barbera (when they directed the marvellous Tom & Jerrys), Grim Natwick, Bob Cannon, Ted Sears, the Fleischers, Walt Lantz, Paul Terry, Shamus Culhane, Bill Littlejohn, Ken Harris, Pete Burness, Emery Hawkins- to mention only a few who were doing animated short subjects- were all working in a field which was a logical extension not only of the motion picture itself, but of the old one-reel live action comedy.
If as a child you drew stick figures on the edge of a tablet or a school book, then flipped the pages to get a spastic and funny little dance, you were animating. Anything beyond that is only sophistication and embellishment. For even today those dancing sticks are absolute in the art of animation, just as the unique essence of the art of painting is the application of pigment to a reasonably flat surface, and the essential isolating quality of sculpturing is a three dimensional representation in some solid material. These are the disciplines that isolate these methods of creativity. Therefore, animation can be created without any embellishment whatsoever, for an audience of one and without a camera. Anything that squiggles, wiggles, waggles, will likely excite in us a feeling of stimulation, an emotional reaction, even a revulsion. We all know that such reactions cannot, or should not be aroused by inanimate things. We should not be angered by a rake when stepped on in the dark since it has no quality of life. Breaking a golf club or throwing a tennis racquet is a natural reaction against seemingly human qualities in an inanimate object. Inanimate objects are diabolically funny indeed in animation. Remember Disney’s piano in Moving Day or the clock in Clock Cleaners or Norman McLaren’s A Chairy Tale?
McLaren’s delightful laughing squiggles and strokes brought universal and deserved praise. Each of us drew our own conclusions as to what the films meant, but very near the surface was an area of response that had very little to do with rationality, and depending upon our area of interest all of us react to other forms of life in quite different ways: a tumor may be beautiful to a pathologist; herpetologists have small, sinewy, evil snakes where other people carry watches; an entymologist may stroke a tarantula with more thoughtfulness and understanding than a parent spends on his own child.
Animation’s potential and scope is literally boundless. In many parts of the world today great experiments in the field are taking pace- new thoughts, ideas, wild flights of fancy, much of it in surface techniques. Color; graphic breakthrough; startling, sometimes shocking in cruel subject matter; animation is being used as political commentary, abstract expressionism, pop and op art experiments, stop live action, painted stones, self-cannibalism, the black experience, textural adventures and sex. Many of these animated films are shown only in garages. But in many countries, notably the United States, most studios have been captured by an avalanche of network demands for low cost Saturday morning television.

One team in Hollywood which once turned out eight to ten seven minute shorts a year now turns out four half-hours a week during the production year, an increase from one hour a year to at least 130 hours, or a 13,000 per cent increase.
A few animators are getting wealthy- which is a happy novelty indeed.
Some of the best work being done in animation, both in the United States and throughout the world, is in the field of animated commercials. Some are brilliant, nearly all are exquisitely timed and cut. This field may be the best training ground available for animators, directors, writers and designers. The disciplines are implicit in the United States: the film is one minute or less, it must tell a story, display a product, make a sales point, have a beginning, middle and an end, be unique yet comprehensible and bear constant repetition.
It is a pity that the experimentalists and the commercial animators could not exchange personnel occasionally, because the disciplines of commercial production would serve the laboratory animator well. Art and experimental and even student films usually run three times too long. The commercial animator would benefit from a little soul-waching and freedom from the very disciplines his opposite needs. The average commercial director would feel grossly sinful if he had an extra 14 seconds to play with.
I believe that every studio that makes a substantial income off this market, or the so-called "kid-vid" market, owes a serious obligation to the future to pour part of it back- five to ten per cent- into training programs, internships, but above all to pure research. The trade unions support the idea; it is just common sense, not altruism.
There is a tendency in the history of any art form when a preoccupation with new instruments or unusual techniques preoccupies the time of the practitioners of that art form, and we get quaint and cacaphonous sounds and sights in our galleries and halls. This is a natural occurance, to be expected and enjoyed, but the tools of the artist have remained very much the same for hundreds of years and I cannot remember when the last valid musical instrument was introduced into an orchestra, perhaps because my father could not remember either.
It is well, I think, to learn from an Edward Steichen, I believe it was, who undertook a photographic assignment from Life magazine limiting him to a 30-year-old Brownie box camera. The result should have surprised no one: a series of exquisite, striking Steichen pictures, because Steichen does not confuse a convenience with a necessity. Steichen and Lincoln’s Matthew Brady are the same cut of man, and each would have flourished in the other’s time.
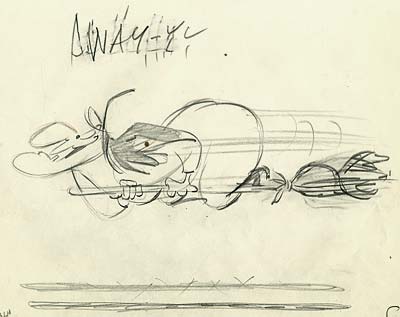
Occasionally, an artist should look at his tools and ask himself what he cannot do without -the essentials- what he must have to pursue his form of expression in animation. In animation as different from other art forms, he must have only three things: a pencil, a number of sheets of paper and a light source. With these things he can animate, without them he cannot.
All other additions are conveniences and embellishments which shade his art form toward others. He does not even need a motion picture camera. The first valid animation, indeed the first motion pictures, were without such cameras. Do you remember the photographic flipping machines at penny arcades?
One of the odd misunderstandings about animation even by those who work in the field is the supposition that an individual drawing in animation has the same importance as doing an illustration.
In animation, drawing is indeed important and great draftsmen as well as great animators are required for such episodes as Bill Tytla’s Night on Bald Mountain or Art Babbitt’s Mushroom Dance. But a single drawing to an animator represents a time interval of 1/24th of a second.
Animation is a chorus of drawings working in tandem, each contributing a part to the whole of a time/space idea. If a single drawing, as a drawing, dominates the action, it is probably bad animation, even though it may be good drawing.

So many of the greatest animators were and are men who became masters of their craft without once having to resort to cleaning up a single drawing. They simply didn’t think that way. Norm Ferguson, the great "Fergie" of Pluto fame who worked in a kind of fluid shorthand, catching the elements of motion in dazzling simplicity, was probably the outstanding example of the animator in his purest form. But Ham Hamilton, Ben Clopton, Ken Harris and many, many others could not draw and found no need to draw, in the conventional sense, which in no way diminishes their artistry; it simply identifies the form.
Different kinds of animation are suitable and correct for the needs of different products. John Halas has been quoted as saying that animation can now get along with four drawings a foot where it once required 24. Actually, animation can get along with no drawings a foot if the subject requirements are such- but it should not be denied 100 drawings per foot if they are needed. The Four Poster required only two actors, but staging Julius Caesar with such restrictions might prove difficult. The point is, if you can only afford two actors, don’t do Julius Caesar.

Animation
The simple question we must ask ourselves about limited animation is this: would we use better animation if we could do so? I contend that the average director on Saturday morning television or in his experimental or laboratory film would rather- far rather- employ the finest animators available and have them deliver not 200 feet but 20 feet a week. And everywhere I have gone in Europe and the Orient the hunger has been for animators, animators in the grand tradition, because a great animator can do anything from a dancing dot to a dinosaur- and every director dreams of working only with great actors, or great animators, as well as great graphics, set designs, lighting and cameramen.
All of us must eventually do what the matador does: go out and face not only the bull, but the crowd. It does the matador little good, provides him little satisfaction to make beautiful passes alone in a moonlit pasture.
If in animation we are to advance our craft we must each eventually face the terror of creativity and each of us must some day do it before the great crowd, for animation is not only an art form, it is also a method of entertainment and a method of communication.

MODERN Animation
We are fortunate, all of us, that animation is so appealing in its verstility. All over the world the most extraordinary things are happening. From Yugoslavia to Japan, South America to, I suppose, Lapland, young men and women are trying new ideas of the most imaginative sort. The medium is springing into life on a thousand fronts with a million facets.
But if we ignore our heritage, if we forget or allow to lapse one of the most important factors, the art of pure animation- a drop of water, a dinosaur, a paramecium, a McLaren dancing line, a blob a silver wind, a silver flute, a beautifully animated, delightfully floating mass of our own introspection- if we forget that these wonders cannot be accomplished by simple means, if we use limited animation only because we can get away with it, then we are overlooking the very essence of our craft and callously destroying history itself.
Chuck Jones
AFI Report (Vol 5, No 2)
Summer 1974
Since Jones wrote this, things have gotten worse, not better. If anyone had the right to complain about the sorry state of modern animation, it was Jones. When you work in the animation industry, and read words like this from a master of the medium, it’s hard not to feel a sense of shame when you see what we put on television today.
Many thanks to Dave Brain for this great article, and thanks to the Van Eaton Galleries for allowing us to digitize these wonderful Chuck Jones drawings for our database.
Stephen Worth
Director
Animation Resources


This posting is part of a series of articles comprising an online exhibit entitled Theory.








 by
by 


![]()